For this assignment, I constructed a 4 bar mechanism using given files to explore their properties. Below is a video of the mechanism with the crank spinning at 20 RPM.
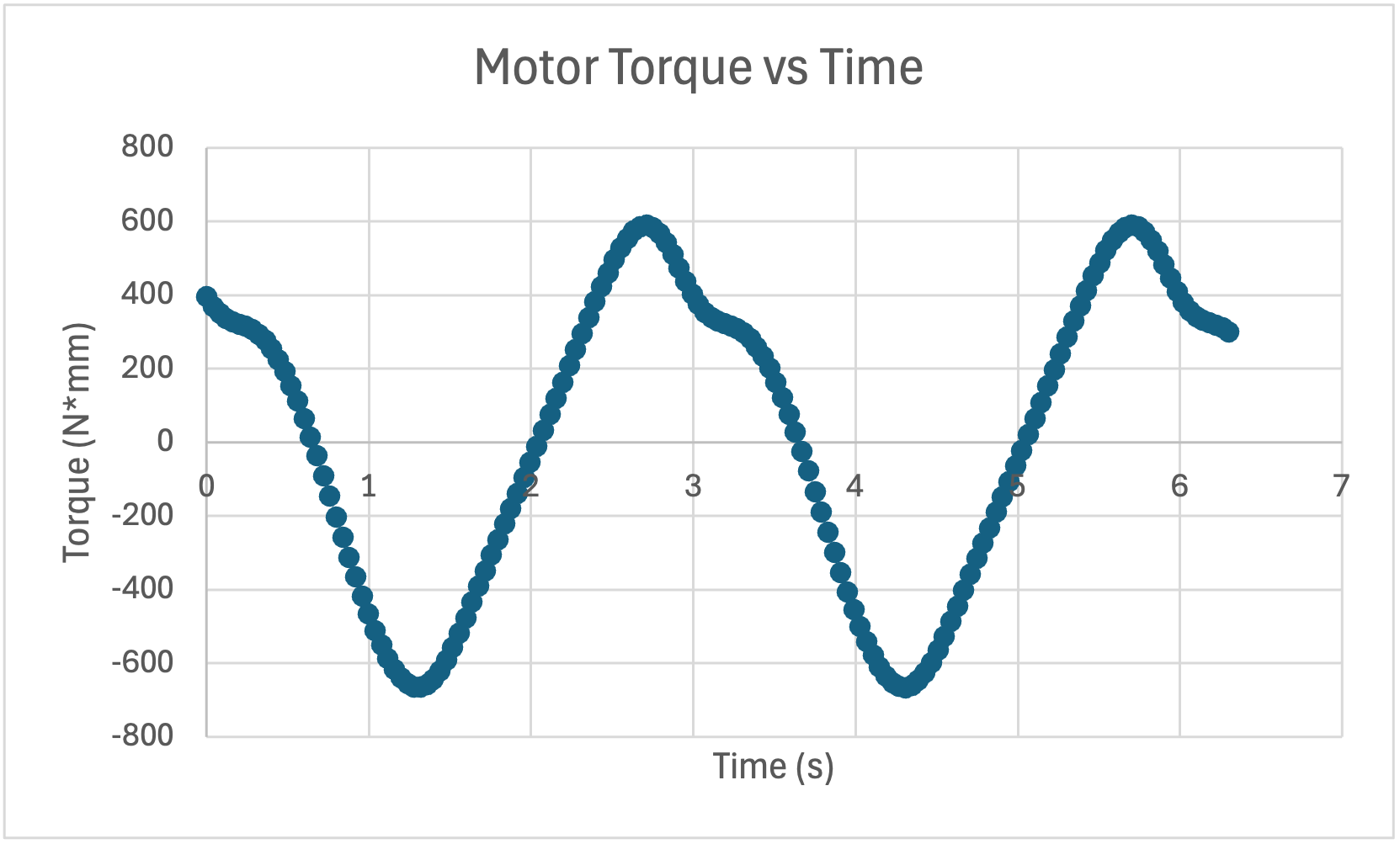
As seen in the graph of motor torque vs time below, the maximum value of the motor torque is -664.30 N*mm. This torque occurs at an angle of -45 deg or 135deg.
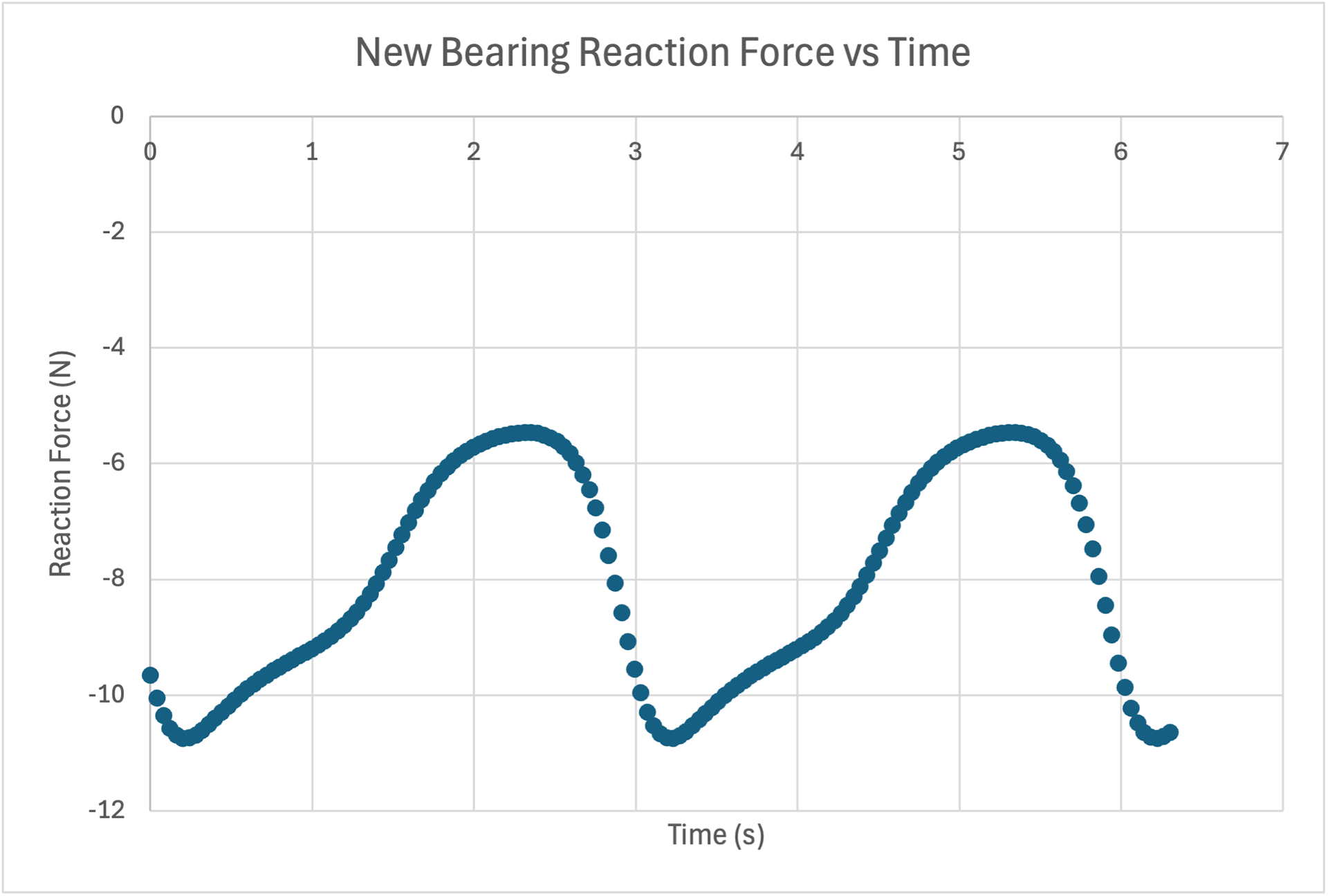
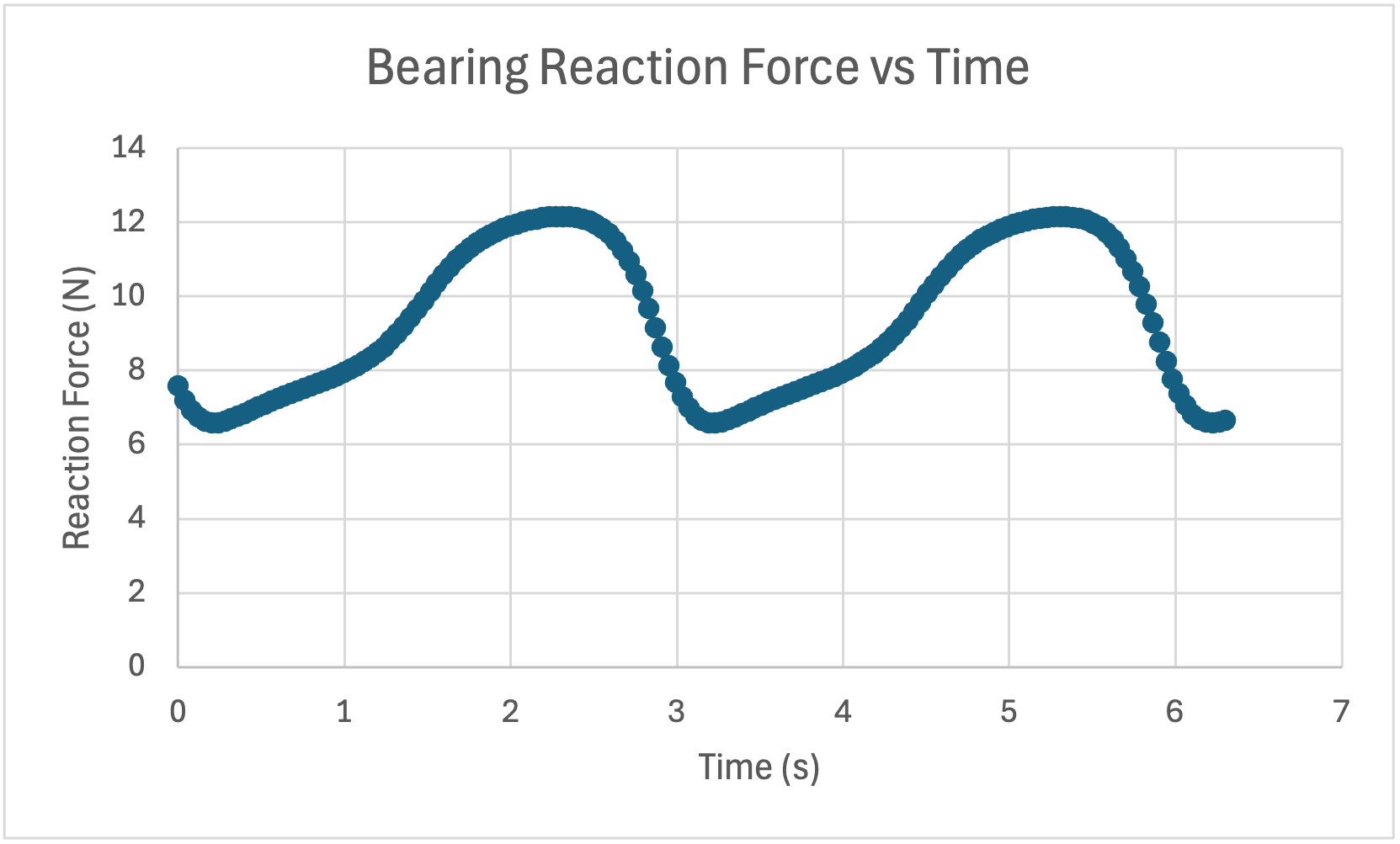
From the reaction force vs time graphs, the maximum vertical force exerted on the NewBearing is -10.75 N. For the Bearing, the maximum vertical force is 12.169 N.
This is a plot of the power consumption (watts) of the motor vs. time, showing how much power the motor consumes over time. As we can see, the power fluctuations and the minimum power required in the beginning is relatively small. But over time, the power required increases greatly. The minimum power required near the end is -1001 W and 539 W (negative sign explanation below). It is interesting to see that for a motor to run at a constant speed of 600 RPM, the power required is not constant.
Negative motor torque is due to the mechanism itself imparting force onto the motor. Due to the simulation including gravity, at some points of motion, the crank or rocker can move without the assistance of a motor by falling down from its own weight. As a result of this, the motor must apply torque in the opposite direction of motion (negative) to keep the crank spinning at a constant 20 RPM. Therefore negative torque means that the motor is effectively slowing down the mechanism.